I) Coal Energy- Most people know coal as a fossil fuel which is used to produce around 40 percent of the world's electricity. It’s a flammable black or brown sedimentary rock, and is made mostly of organic carbon. It is used primarily as an energy source, either for heat or electricity. It was once heavily used to heat homes and power locomotives and factories.The most significant uses of coal are in electricity generation, steel production, cement manufacturing and as a liquid fuel. Around 6.6 billion tonnes of hard coal were used worldwide last year and 1 billion tonnes of brown coal. Since 2000, global coal consumption has grown faster than any other fuel.
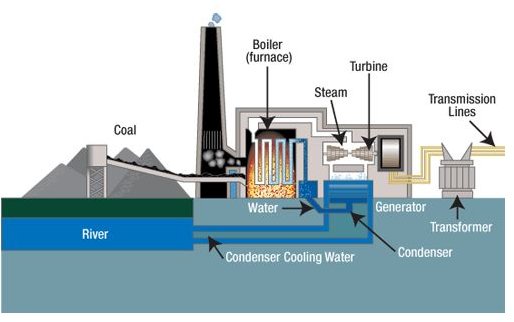
The coal-fired steam station, works much like a nuclear station where water is turned into steam, which in turn drives turbine generators to produce electricity. Basically, heat is created then water turns to steam, the steam turns the turbine and finally the steam turns back into water. The cooling water is returned to its source without any contamination, and the steam water is returned to the boiler to repeat the cycle.
Pros/Benefits:
-inexpensive
-abundant supply especially in industrialized countries
-low capital investment compared to gas or nuclear
-continuous power, good utilization, high load factor
-can be converted into a liquid or a gas, which burn cleaner
-can be made low carbon and clean with CCS and various scrubbers
Cons/Drawbacks:
-coal is nonrenewable. Finite supply
-coal contains lots of CO2 per BTU, largest contributor to global warming
-devastation of environment around coal mines
-high cost of transporting coal to centralized power plants
-coal ash is a hazard and a disposal problem
-severe environmental, social, health and safety impacts of coal mining
-second highest emitter of methane
-clean coal is not carbon free
-high levels of radiation
-coal burning releases SOx and NOx which both cause acid rain
-burning coal emits mercury and other heavy metals that pose health risks
-coal emissions linked to increased rates of asthma and lung cancer
II)Solar Energy- Is energy emitted from the sun which is converted to electricity for your home. It can be used in ventilation, heating swimming pools, heating water, heating/powering homes, power pumps, battery charging and more. Additional uses can be using solar energy for cooking, indoor lighting and outdoor lighting.

It works by converting sunlight to electrical power. Solar power cells convert sunlight into electricity, using the energy of speeding photons to create currents within a solar panel. Photons are created in the centre of the sun by the fusion of atoms.
Pros/Benefits:
-renewable, no fuels required
-operating costs are low
-non-polluting. Carbon-free except for production and transportation
-can utilize thermal storage to better match supply with demand
-high efficiency
-scalable to the 100 MW+ level
-can serve as a drop-in replacement for conventional fuels to make steam
Cons/Drawbacks:
-intermittent
-low energy density
-construction/installation costs are high
-slightly more expensive than solar PV
-relatively new technology involved
-heavily location dependant
-manufacturing processes often create pollution
-require lots of space
-hard to compete against very cheap natural gas
-some people find them unattractive
III) Wind Energy- Wind energy can be used for anything from power on boats, battery charging, or electricity to be used commercially. Wind energy is known to be used as early as 200 B.C. Original windmills were used in the Middle East in areas such as what is now known as Iran, and areas in Afghanistan.Wind turbines can convert the energy in the wind into mechanical power that can be used for a variety of activities like pumping water. Wind turbines can also use generators to convert wind energy into electricity.
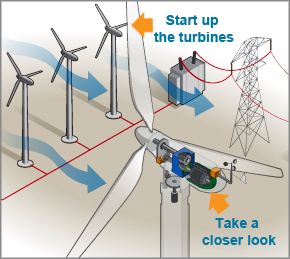

Wind turbines operate on a simple principle. The energy in the wind turns two or three propeller-like blades around a rotor. The rotor is connected to the main shaft, which spins a generator to create electricity.
Pros/Benefits:
-renewable and sustainable
-costs are low and continue to decrease
-low life cycle carbon footprint
-power is essentially free once infrastructure is paid for
-abundant domestic supply
-can be used almost anywhere
-clean energy, no fuel to drill, mine, transport or burn
Cons/Drawbacks:
- wind is inconsistent, unsteady and unpredicatable
-wildlife impact for instance birds have experienced fatalities
-some people complain of noise from turbines
-wind power is not cheap and like other energy sources, rely on the government
-wind farms are generally located in rural areas that might be otherwise picturesque
-localized impact on night-time temperatures and weather
No comments:
Post a Comment